Introduction: AI’s promise vs. reality
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been heralded as a game-changer for businesses, promising to transform industries, boost efficiency, and unlock unprecedented innovation. Yet, the reality is more complex: while 98% of companies are exploring AI, only 26% have successfully moved beyond pilot projects to create real value.
A recent report by Boston Consulting Group (BCG) highlights this disconnect, underscoring the barriers organizations face in scaling AI and the critical factors that distinguish successful adopters. This post explores these challenges and offers actionable insights to bridge the gap, helping businesses maximize their AI investments.
The common barriers to AI success
Despite substantial investments, many organizations face difficulties in making AI beneficial for them. BCG revealed several key challenges, from a lack of strategic alignment to an excessive emphasis on algorithms and the latest technologies.
Often, companies treat AI as a buzzword and chase numerous disconnected projects, hoping to explore its transformative potential. The initial focus is often too much on testing out the latest technology, without articulating a cohesive vision that leverages the company’s strengths and weaknesses, considers its market position, anticipates the use of AI technology by other industry players, or considers internal stakeholders.
The results in this case are typically disappointing and costly, often hindering further adoption due to a lack of tangible outcomes, along with poor integration into existing processes, IT systems, and broader business strategies. All exacerbated by issues like inconsistent data quality, security concerns, and resistance to change can derail efforts.
The most successful AI initiatives rely on a blend of technical expertise and organizational readiness. However, many businesses lack skilled AI professionals and struggle to improve AI literacy across their workforce. Without reimagining workflows and investing in change management, even the best AI systems can fail to deliver.
What successful companies do differently
The 26% of companies thriving with AI adoption share distinct characteristics that set them apart. Here’s what they do differently:
- They prioritize a handful of high-value initiatives that align with their core business objectives.
- Leaders allocate resources thoughtfully—70% to people and processes, 20% to technology, and just 10% to algorithms.
- They build infrastructure that supports scalable AI solutions while rapidly iterating on pilots to refine their impact.
- By investing in AI literacy and fostering a culture of innovation, they empower employees to embrace and leverage AI effectively.
- Beyond cost-cutting, these companies use AI to create new revenue streams, optimize core operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Managing expectations and addressing common barriers
From our experience working with clients, we see a mix of these common barriers highlighted by BCG. Two key challenges stand out: skills and process gaps and integration and scalability hurdles. These are critical areas where organizations often falter. A major factor slowing adoption is a lack of knowledge about the boundaries of AI systems. Generative AI applications are particularly susceptible to inflated expectations, with many customers anticipating near-perfect accuracy from the outset. However, due to the probabilistic nature of these systems, achieving a 100% success rate is inherently difficult. Mismanagement of these expectations can lead to frustration and disillusionment.
One way we’ve successfully addressed expectation and ROI challenges is illustrated by a recent customer service automation project that we've completed. Rather than attempting to automate every possible query, we focused on automating 60% of tickets that are repetitive and well-suited for AI automation. Examples include inquiries regarding order statuses, return policies, or troubleshooting guides - all implemented within a month.
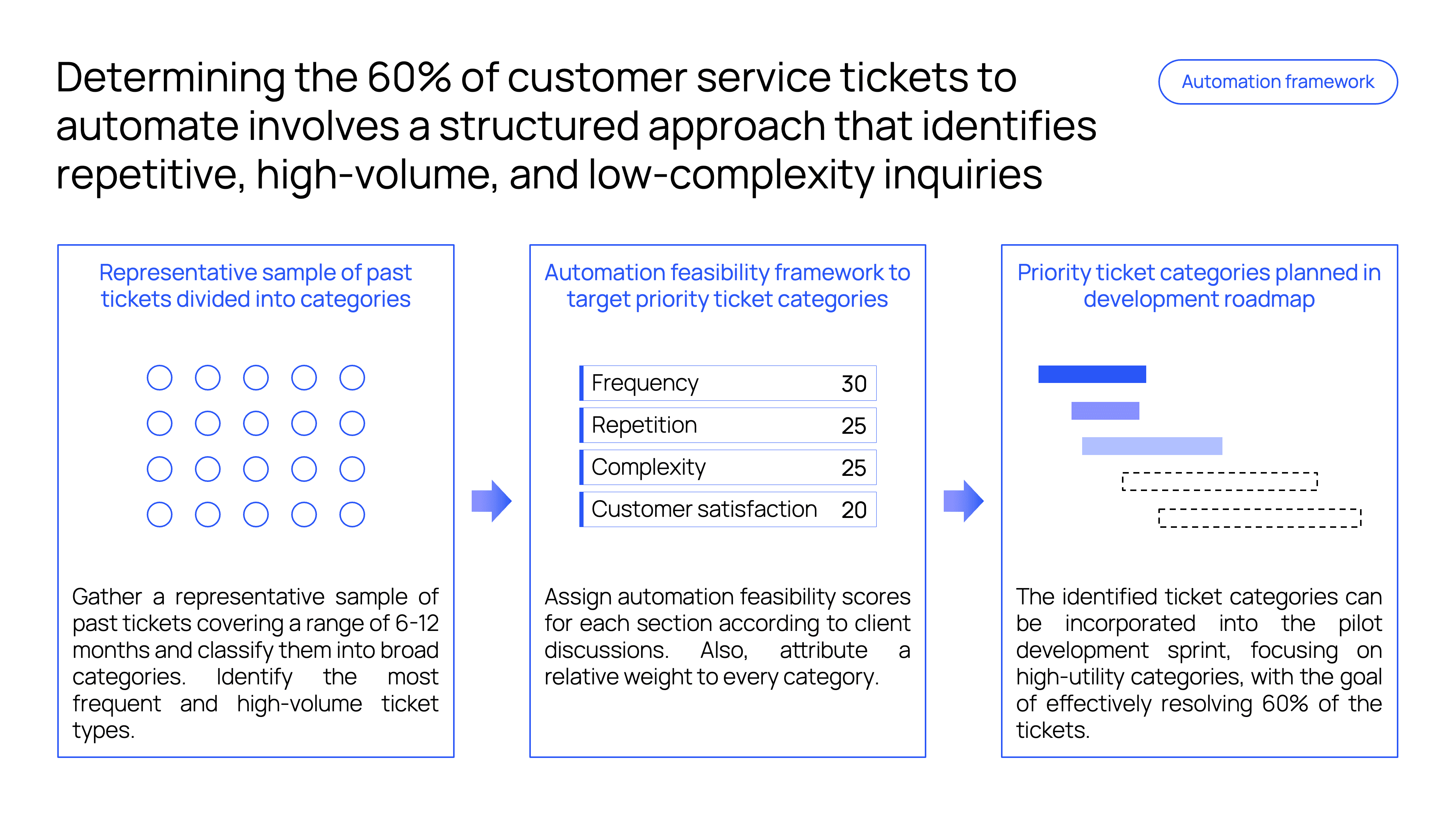
This focused approach delivers immediate efficiency gains, ensuring a clear return on investment from the outset. By prioritizing well-suited, repetitive queries, it mitigates the risks associated with prematurely addressing complex edge cases, which can undermine confidence in the system. The tangible results achieved early on foster trust, creating a solid foundation for implementing further AI automation initiatives.
How you can apply this strategy
To implement AI effectively and maximize its impact, organizations must embed AI efforts into their broader business strategy, aligning with key objectives and market dynamics. Avoid the common pitfall of experimenting with disconnected AI projects or adopting the latest technologies without a clear vision.
Analyze processes to uncover repetitive, high-volume tasks or decision-making bottlenecks where AI can create measurable value. Prioritize use cases that align with your organization’s unique strengths and position in the market, ensuring they are both practical to execute and strategically significant. Begin with one or two well-defined use cases that offer tangible benefits and are feasible to implement within existing systems. Treat these pilots as both quick wins and stepping stones for building internal AI expertise, data pipelines, and scalable frameworks.
Meanwhile, ensure that the organization becomes fluent in AI. Do not treat it as a black box technology and actively promote experimentation. Incorporate risk management into your AI strategy, addressing issues like data security, algorithmic bias, and resource allocation early in the process. Keep an eye on industry trends and competitor moves to position your AI initiatives as a source of differentiation.
By starting small, achieving tangible results, and integrating AI into your broader strategy, you’ll not only demonstrate value but also create the foundation for a scalable and sustainable AI ecosystem.
In addition, organizations must recognize that the first iteration of a GenAI application does not need to be perfect. Instead, the focus should be on delivering incremental improvements and building trust over time. That being said, there are several steps AI developers can take to make GenAI applications more reliable and trustworthy.
Making GenAI applications more trustworthy
In designing trustworthy LLM-based applications, we emphasize pragmatic and deterministic approaches to ensure reliability and scalability. Breaking complex tasks into smaller, manageable components, employing assertion-based validations, and involving humans in the loop are critical principles that provide fine-grained control over AI workflows and enhance overall system performance.
This thinking underpins much of our work, including the GenAI Launchpad, where we treat AI systems as structured pipelines that allow for granular control at every step. By using router and task components, we enable users to customize workflows and handle a wide range of workloads efficiently. Decomposing AI systems into smaller, focused components not only improves performance but also ensures that each task has a clear objective, aligning well with the strengths of LLMs.
A balanced path to success
The journey to successful AI adoption requires a blend of technical excellence, realistic goal-setting, and continuous iteration. While challenges like integration and scalability hurdles persist, focusing on skills development, operational workflows, and trust-building measures can set organizations on the right path. Essentially, AI works best when technical accuracy is paired with a clear understanding of its limitations. By setting realistic expectations and focusing on building reliable and scalable systems, businesses can create value with AI.
Ready to unlock AI’s potential?
Are you looking to scale your AI initiatives or overcome common barriers to adoption? At Datalumina, we specialize in helping organizations bridge the gap between promise and reality.
Contact us today to explore tailored solutions for your business.




